In today's digital age, connectivity has become the backbone of our society, enabling seamless communication, innovation, and collaboration. As we look towards the future, the convergence of 5G technology and edge computing holds immense potential to revolutionize connectivity infrastructure. This blog explores the transformative impact of this convergence on various industries and examines the opportunities and challenges it presents.
Understanding 5G and Edge Computing
Before delving into the intersection of 5G and edge computing, it's essential to understand the individual technologies. 5G is the fifth generation of cellular network technology, offering significantly faster data speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to its predecessors. On the other hand, edge computing involves processing data closer to the source of generation, reducing latency and enhancing efficiency by bypassing the need to transmit data to centralized cloud servers.
The Synergy of 5G and Edge Computing
The integration of 5G and edge computing represents a paradigm shift in connectivity infrastructure. By leveraging the low latency and high bandwidth capabilities of 5G networks along with the localized processing power of edge computing, organizations can unlock new possibilities for real-time data analytics, immersive experiences, and mission-critical applications.
Benefits of 5G and Edge Computing Integration
- Enhanced Speed and Performance: The combination of 5G and edge computing enables faster data processing and reduced latency, leading to improved performance for applications such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and telemedicine.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Edge computing architecture allows for distributed computing resources, enabling scalability and flexibility to meet evolving connectivity demands in dynamic environments.
- Cost Efficiency: By minimizing data transmission to centralized servers, edge computing reduces bandwidth usage and operational costs, making it a cost-effective solution for handling large volumes of data.
- Improved Reliability: The decentralized nature of edge computing enhances system reliability by reducing the impact of network outages and latency issues, ensuring continuous operations in mission-critical scenarios.
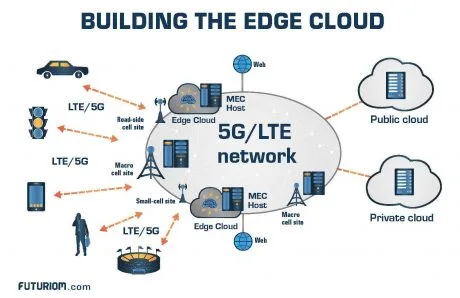
How does Edge Computing Improve Network Latency in 5G?
Edge computing plays a crucial role in reducing network latency in 5G by processing data closer to the end-user or device. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data travels back and forth between the device and centralized servers, edge computing locates computing resources closer to the data source. This proximity significantly reduces the time it takes for data to travel, resulting in lower latency and faster response times. As a result, applications and services that require real-time interaction, such as video streaming, online gaming, and IoT devices, benefit from improved performance and user experience.
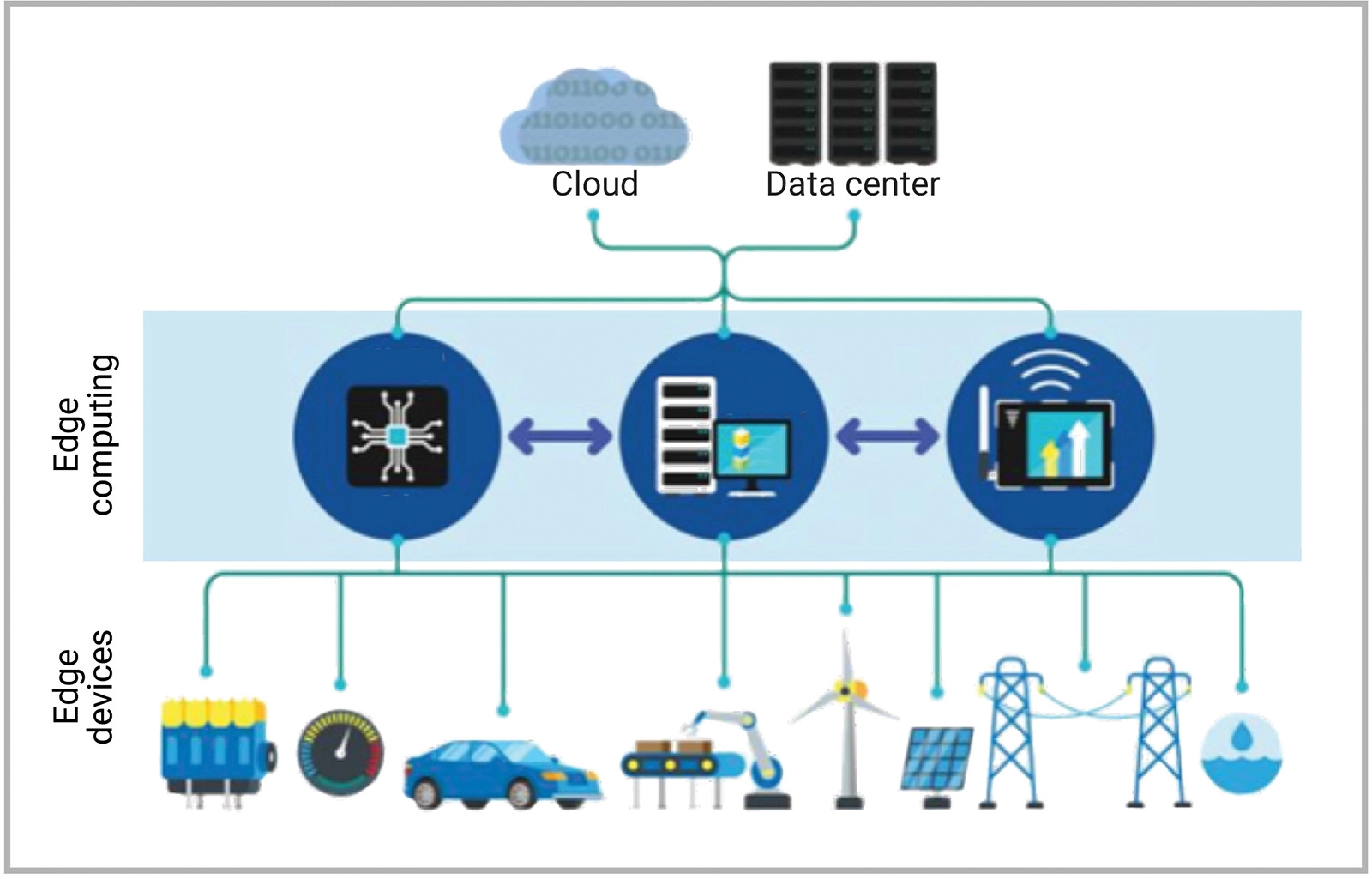
What role does Edge Computing play in the Future of IoT?
Edge computing is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of the Internet of Things (IoT). As the number of connected devices continues to grow exponentially, traditional cloud-based IoT architectures face challenges such as latency issues, bandwidth constraints, and privacy concerns.
Edge computing addresses these challenges by moving data processing closer to IoT devices, enabling real-time data analytics, faster response times, and reduced reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure. This decentralized approach enhances the scalability, reliability, and security of IoT deployments, making edge computing an essential enabler of IoT innovation and growth.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its immense potential, the integration of 5G and edge computing also presents certain challenges and considerations:
- Security Concerns: The distributed nature of edge computing introduces new security risks, requiring robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying 5G networks and edge computing infrastructure requires significant investment in hardware, software, and network upgrades.
- Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility and interoperability between 5G networks and edge computing platforms is crucial for seamless integration and optimal performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must navigate regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements related to data privacy, network standards, and spectrum allocation when deploying 5G and edge computing solutions.
Future Applications and Industries Impacted
The convergence of 5G and edge computing is poised to transform various industries and applications, including:
- Smart Cities: Enhanced connectivity and real-time data processing capabilities enable the development of smart city initiatives such as traffic management, public safety, and environmental monitoring.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and real-time diagnostics benefit from the low latency and high bandwidth of 5G and edge computing, improving healthcare access and outcomes.
- Manufacturing: Edge computing enables predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization in manufacturing operations, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles, intelligent transportation systems, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication rely on 5G and edge computing for real-time decision-making and coordination.
Conclusion:
As we embark on the journey towards the future of connectivity, the convergence of 5G and edge computing promises to unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and connectivity. By harnessing the power of these transformative technologies, organizations can drive digital transformation, enhance user experiences, and pave the way for a smarter, more connected world.